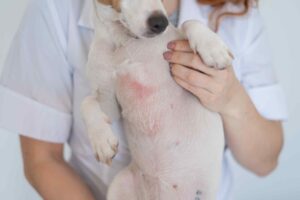
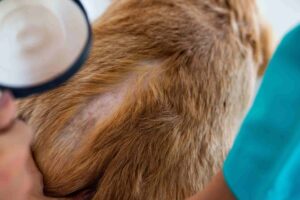
Studying atopic dermatitis in dogs would seem to be a valid and transferable model for understanding its dynamics in humans. Indeed, the pathophysiological features, response to antibiotic therapy, and changes in the skin microbial profile have shown remarkable similarities .
This is according to Domenico Santoro and Aline Rodrigues Hoffmann in a recently published commentary in Journal of Investigative Dermatology where they summarized the main evidence supporting the use of canine models for the study of this disease. Let’s look at the main points.
Thanks to recent advanced genomic investigation techniques, the skin microbiome has fewer and fewer secrets.
Indeed, well known is the typical bacterial composition of the microorganisms that populate our skin as well as their inter- and intra-variability among different parts of the body for example. Confirmed then are its alterations in case of diseases, atopic dermatitis (AD) included.
Also increasing in parallel is knowledge in the veterinary field. For example, the skin of dogs showed a microbiota that was quite similar in compositional characteristics, in response to treatment, and in disease situations.
Atopic dermatitis and skin microbiota
Here’s why.
- Dogs are naturally affected by AD with clinical and immunological similarities to humans
- During the active phase of disease there is an increase in the genus Staphylococcus in both cases. However, while in dogs the aggravation of the disease is attributed to S. pseudintermedius and in, in humans (children especially) it is related to S. aureus . In both dogs and humans, however, involvement, albeit to a lesser extent, of Corynebacterium
- in the presence of AD, in both humans and dogs the diversity of skin microbiota in that area decreases. Significant differences with controls were in fact reported by Bradley et al. (2016). However, antibiotic therapy has been shown to restore the starting balance by increasing the overall diversity and reducing the abundance of Staphylococcus spp. However, the solution is temporary with a new decrease in diversity in dogs with AD once treatment is stopped. Also impaired epidermal barrier function with reduced trans-epidermal water levels. Differences also in skin pH compared with controls
- Similar pathological features have been recorded on children with AD by Kong et al. (2012). Indeed, the diversity of the microbiome has been shown to be reduced with, on the other hand, a marked increase in disease-related species, S. aureus in primis. Following intermittent treatment with anti-inflammatories or antibiotics (oral or topical), diversity showed similar values to controls with reduced levels of Staphylococcus spp. and Corynebacterium
In general, the correlation between atopic dermatitis and skin dysbiosis has been shown to be strong in both humans and dogs .
Whether this is a cause or a consequence, however, remains to be demonstrated. Insights are also needed into the relationship between the pathology and the innate immune response, which is also altered in both species.