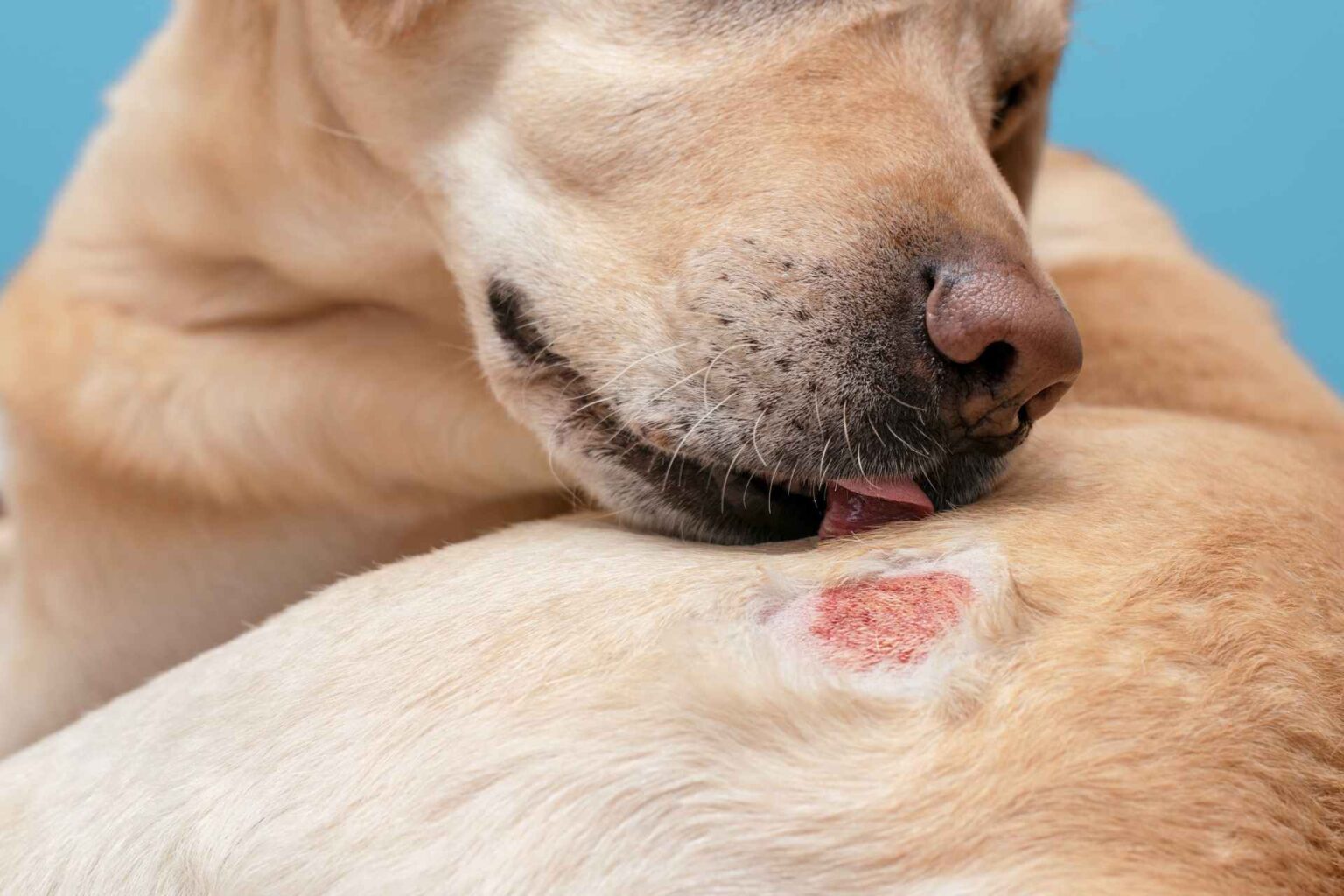
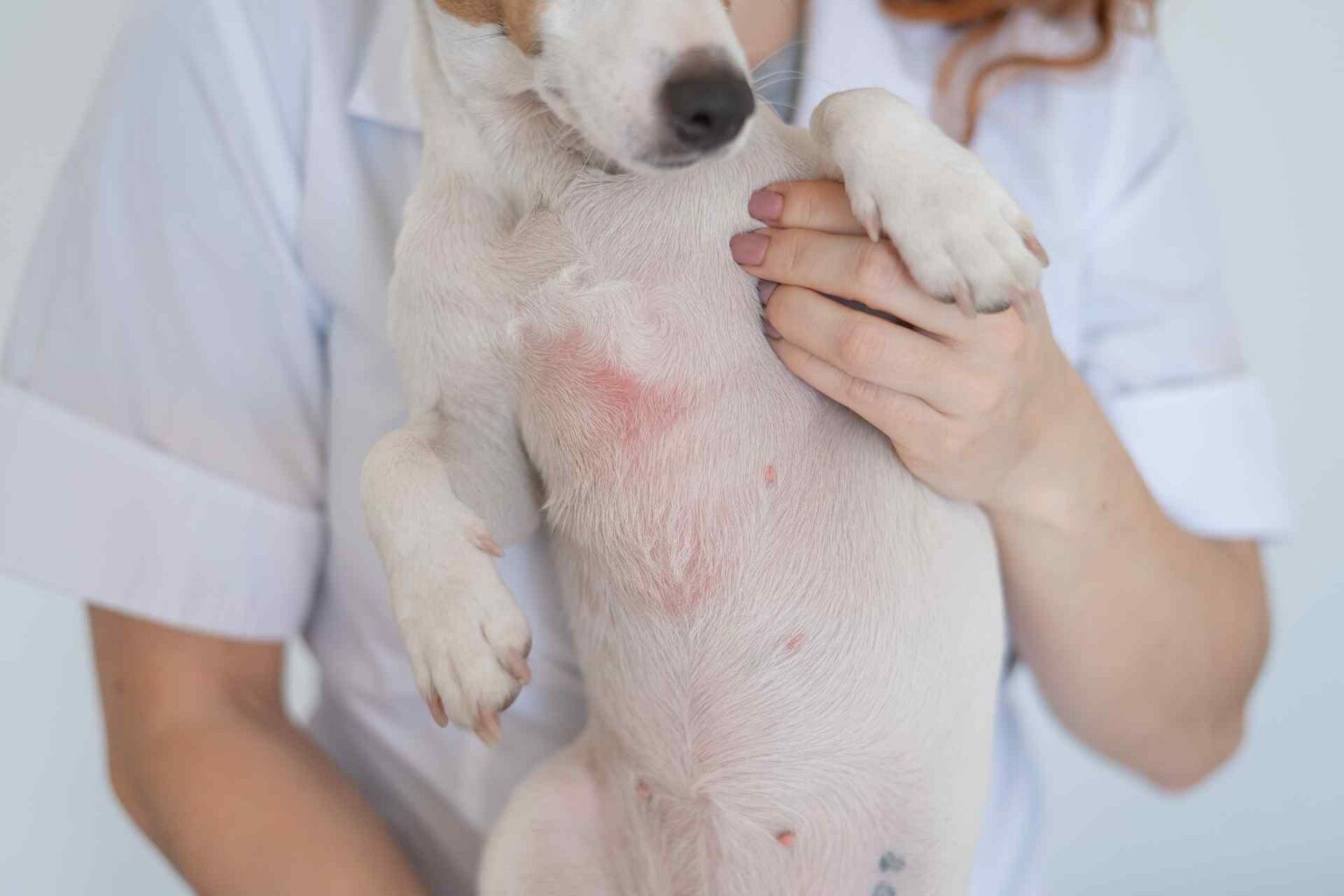
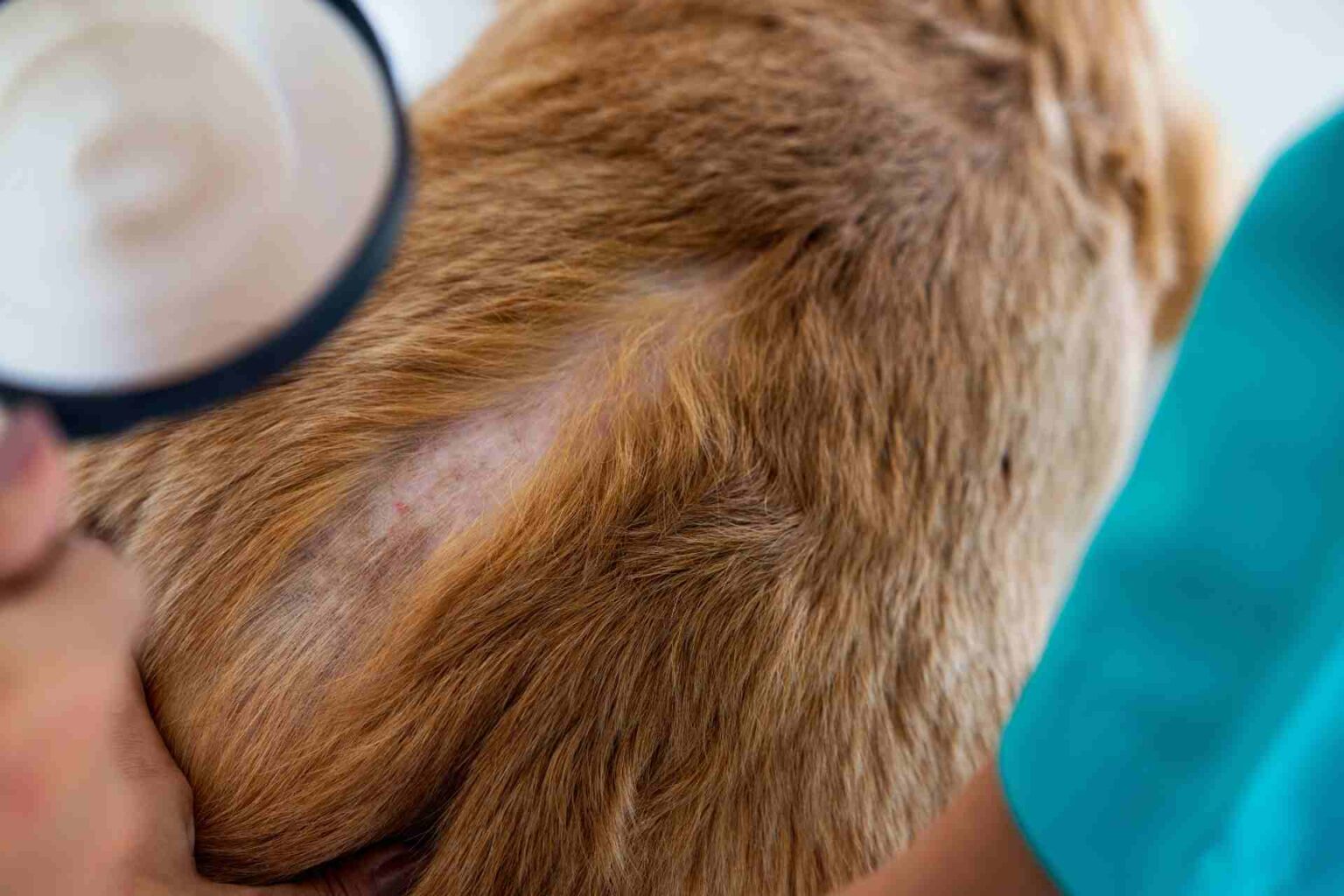
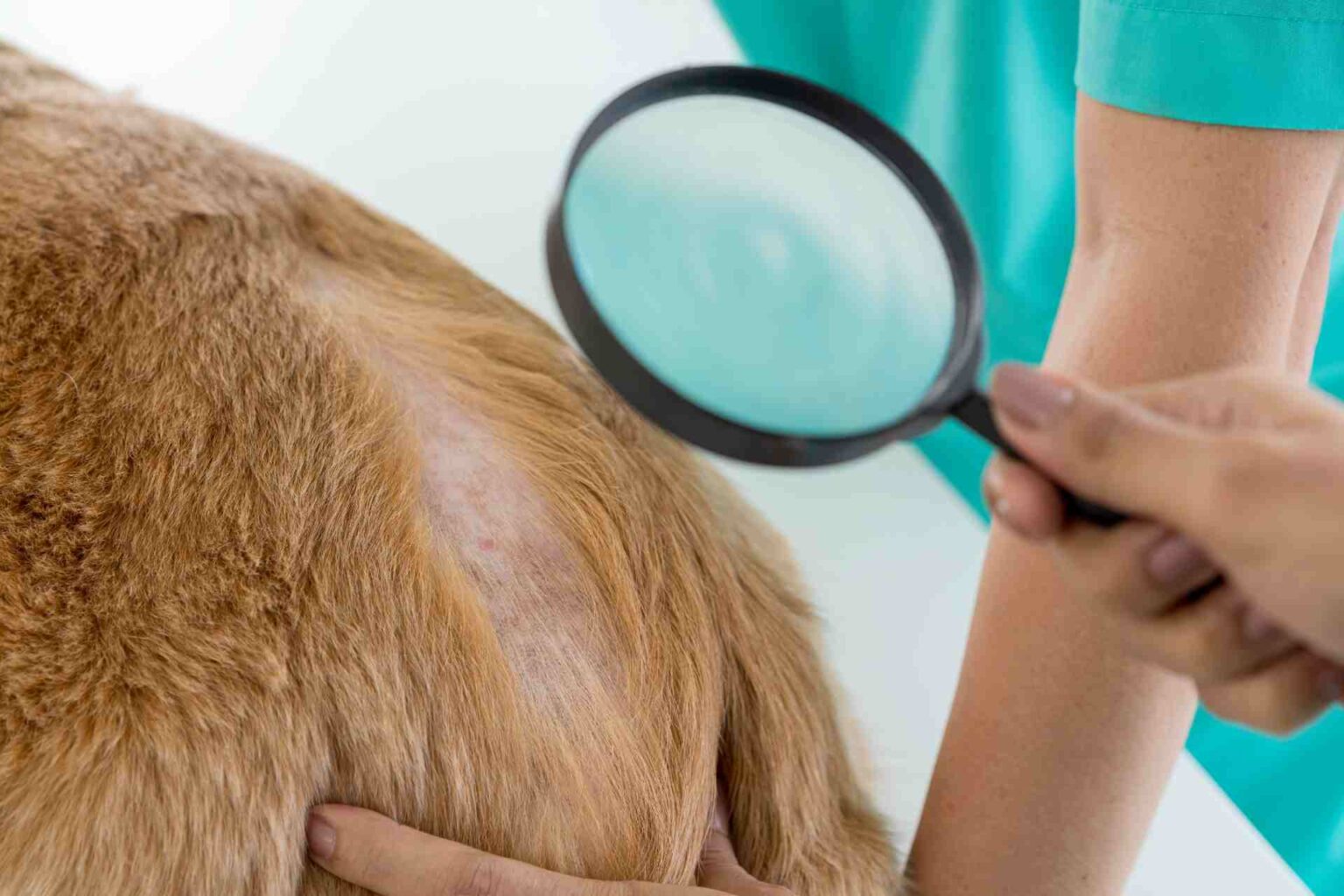
Zinc is an important modulator of several essential biological functions; several studies have shown that in dogs a diet deficient in zinc leads to decreased blood concentrations of this trace element with skin manifestations such as: dull, rough coat and lesions on the abdomen and hind limbs. Lesions initially occur in the friction areas with pustules, boils, scabs, and scales.
Zinc deficiency is also manifested by poor appetite, loss of taste and smell, and, in the long term, weight loss, conjunctivitis, cheilitis, and decreased healing. At the immune level, there is decreased T-cell response, lymphopenia, and decreased chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and macrophage activity.
Clinical case: 12-year-old male dog
Report: Ronnie, a 12-year-old male whole mixed-breed dog is referred for dermal lesions that have never gone into remission for about four years.
Reason for examination: subject has hyperpigmented areas with rarefaction of hair and alopecic and malodorous areas on limbs, groin, ear pinnae, periocular and labial area, lichenification at the level of the muzzle and forearms, and licking lesions related to low-grade itching. The dog’s weight is 27 kg with a BCS of 4/9.
Clinicalhistory: hypothesized Leishmania positivity in the past and case treatment protocol was prescribed.
Subsequently, further, more in-depth analysis disproved the results of the rapid serological test. The therapy is changed, an immunological therapy drug is added, but no improvement is seen. Further dermatological investigations are performed, which by scotch test detect overgrowth of Malassezia. An antifungal, topical and antiparasitic treatments are administered at this point in conjunction with a commercial hydrolyzed protein diet.
Not noticing no improvement, antibiotic and cortisone is administered; again there will be no improvement.
Treatment: failing to obtain resolution of lesions, the veterinarian suspended all treatment and decided to put Ronnie on monotherapy with Zincogen Pet Ultra (NBF Lanes) complementary feed intended for special nutritional purposes, high in essential nutrients and highly digestible ingredients. With lysine, nucleotides, vitamin C and mannan oligosaccharides.
This product is chosen because it contains microencapsulated zinc, which prevents vomiting episodes. It also contains Enterococcus faecium as a probiotic and Echinacea angustifolia, which in addition to having immune-stimulating properties, inhibits the enzyme jaluronidase and stimulates fibroblast proliferation.
An extraordinary achievement
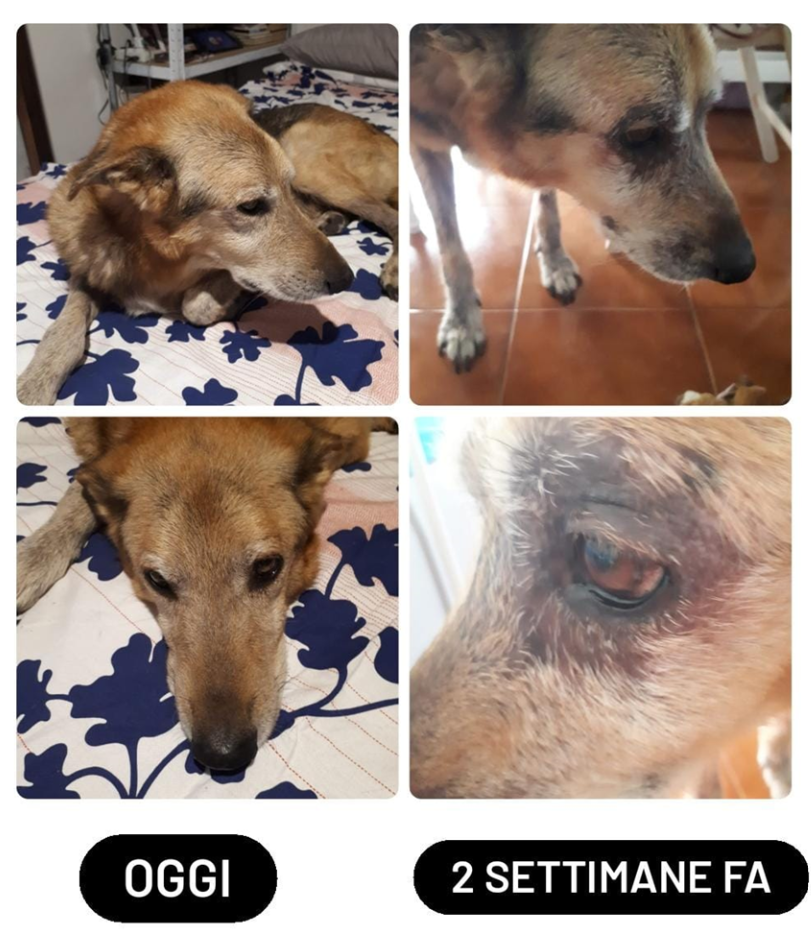
Follow-up: After 2 weeks of Zincogen supplementation, the owner sends the veterinarian photos of the extraordinary and especially rapid improvement in Ronnie’s clinical picture. The improvement was significantly faster than expected.
The doctor decided to continue Zincogen for an additional two months and replace the commercial hypoallergenic diet with a commercial single-protein complete food.
Take home message: The case report suggests to us that essential fatty acid (EFA) and zinc supplementation should be evaluated in conjunction with further therapy in a subject with dermatological problems, even if caused by Leishmania.
Giulia Pignataro and Francesca Della Monica
Reference
Francesca Della Monica. Final thesis of Master’s degree II level in “Nutrition and Clinical Dietetics of the Dog and Cat” of the University of Teramo, Academic year 2021 – 2022