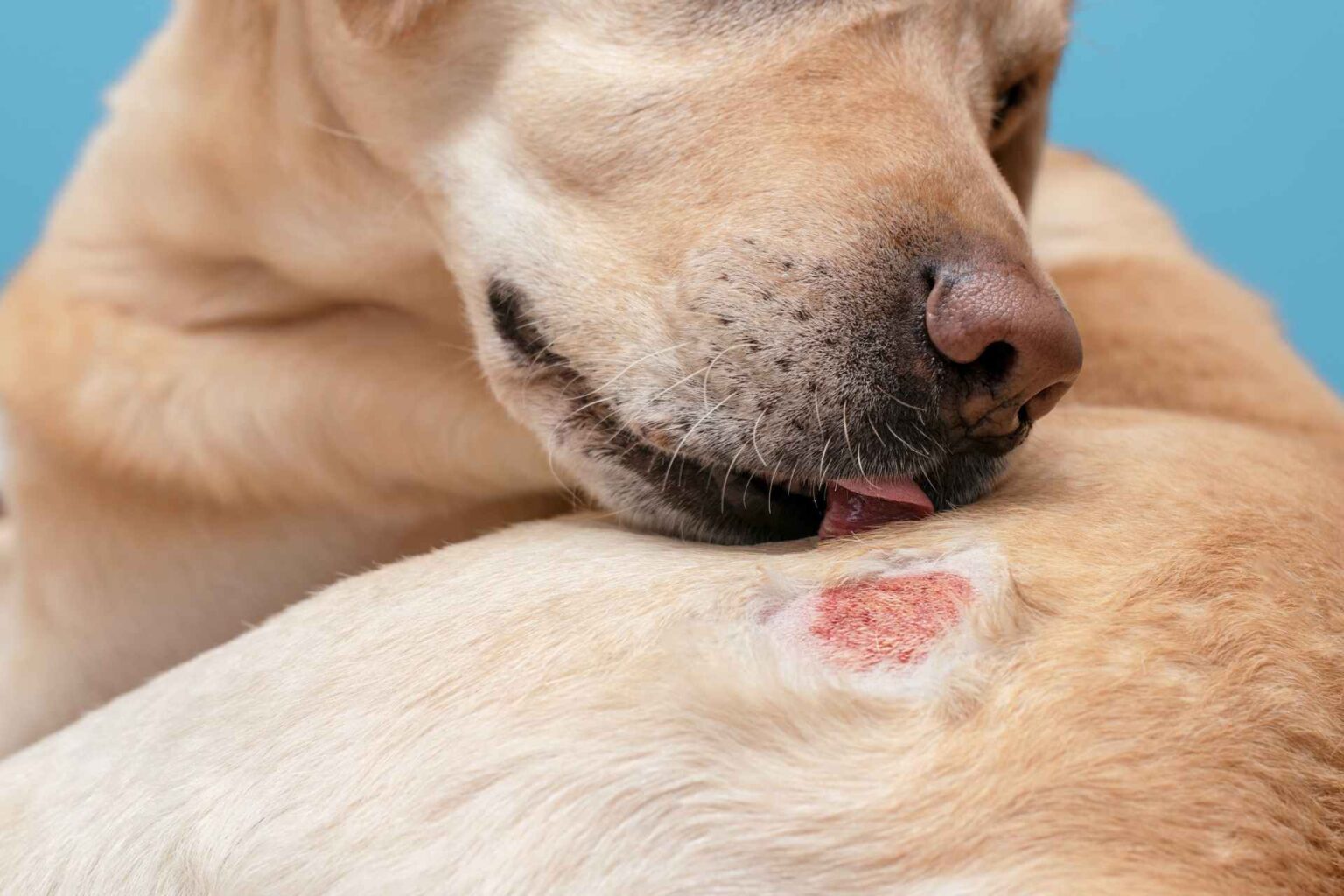
Canine atopic dermatitis (CAD) is a common inflammatory and itchy allergic skin disease characterized by excessive production of IgE immunoglobulins directed against allergens. Because of the multifactorial nature of this condition, multimodal and highly specific treatment regimens are often indicated for the particular clinical case.
Cannabinoids are a group of compounds found in the plants of Cannabis sativa. Cannabidiol (CBD) is the predominant nonpsychotropic cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the precursor carboxylic acid of CBD, and recent studies have shown its effective absorption, perhaps even better than CBD itself. Various studies have shown immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects associated with these molecules, which also appear to be, in addition, well tolerated and effective in reducing, in dogs, osteoarthritis pain.
CBD does not appear to interact directly with receptors of the CB1 or CB2 endocannabinoid system, but it does succeed in altering endogenous endocannabinoid levels. In addition, CBD may also interact with other components related to the receptor system in inflammatory mediating cells or neurons, such as adenosine reuptake inhibitor and peroxisome proliferation receptors (PPARs).
Cannabinoids against canine atopic dermatitis
To date, there are no studies in the literature that have investigated the efficacy of CBD and CBDA for the treatment of CAD. To this end, the study by Loewinger et al. aimed to determine whether hemp extract, rich in CBD/CBDA, could reduce itching and skin lesions in dogs with CAD.
Secondary objectives of the study included investigation of possible adverse effects of this treatment through serum biochemical tests.
The randomized study, double-blind, placebo-controlled, enrolled 32 dogs with CAD that were randomized to receive either 2 mg/kg of a CBD/CBDA mix or placebo for a period of 4 weeks. Dogs were evaluated at day 0 (day of enrollment, D0), day 14(D14) and day 28(D28). The pVAS scale was used to assess the severity of the animal’s itching, and the CADESI-04 index was used to assess the lesions caused by CAD.
The results showed that there was no significant difference from D0 to D14 or D28, according to the CADESI-04 index, in terms of CAD injury in both study groups .
The pVAS scores were significantly lower for the CBD/CBDA group at D14 and D28 compared with the placebo group, and a significant reduction in pVAS was also observed at D14 compared with baseline (D0), but only in the CBD/CBDA group.
Between the two study groups, there was also no significant difference in serum levels of IL-6, IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein -1, IL-31 or IL-34 at D0 or D28.
Regarding adverse events, no particularly worrisome data emerged, none of the dogs had to discontinue treatment during the study, and most owners said they would use the product again under treatment.
Cannabidiol as an adjunctive therapy
In the study by Loewinger et al. CBD at 2 mg/kg twice daily was well tolerated with minimal adverse events. Data suggest, therefore, that CBD as an adjunctive therapy may be helpful in relieving itching in dogs with CAD.
Reference
Loewinger M, Wakshlag JJ, Bowden D, Peters-Kennedy J, Rosenberg A. The effect of a mixed cannabidiol and cannabidiolic acid based oil on client-owned dogs with atopic dermatitis. Vet Dermatol. 2022 Aug;33(4):329-e77. doi: 10.1111/vde.13077. Epub 2022 May 29.